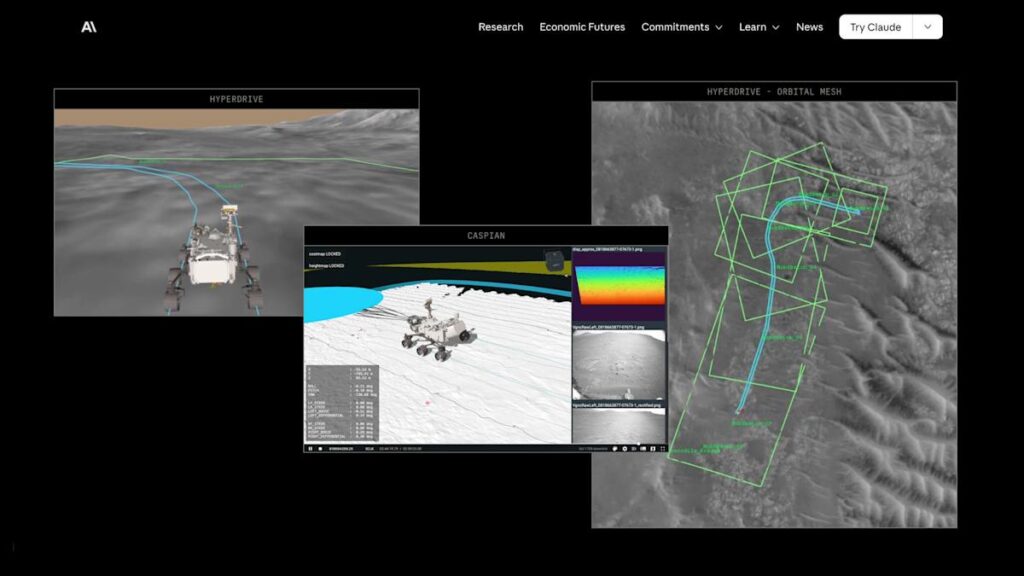
Since 2021, NASA’s Perseverance rover has achieved quite a few historic milestones, together with sending again the primary audio recordings from Mars. Now, practically 5 years after landing on the Red Planet, it simply achieved one other feat. This previous December, Perseverance efficiently accomplished a route by means of a piece of the Jezero crater plotted by Anthropic’s Claude chatbot, marking the primary time NASA has used a big language mannequin to pilot the car-sized robotic.
Between December 8 and 10, Perseverance drove roughly 400 meters (about 437 yards) by means of a subject of rocks on the Martian floor mapped out by Claude. As you may think, utilizing an AI mannequin to plot a course for Perseverance wasn’t so simple as inputting a single immediate.
As NASA explains, routing Perseverance is not any simple process, even for a human. “Each rover drive must be rigorously deliberate, lest the machine slide, tip, spin its wheels, or get beached,” NASA mentioned. “So ever because the rover landed, its human operators have painstakingly laid out waypoints — they name it a ‘breadcrumb path’ — for it to observe, utilizing a mix of photographs taken from house and the rover’s onboard cameras.”
To get Claude to finish the duty, NASA needed to first present Claude Code, Anthropic’s programming agent, with the “years” of contextual knowledge from the rover earlier than the mannequin may start writing a route for Perseverance. Claude then went in regards to the mapping course of methodically, stringing collectively waypoints from ten-meter segments it might later critique and iterate on.
This being NASA we’re speaking about, engineers from the company’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) made positive to double examine the mannequin’s work earlier than sending it to Perseverance. The JPL crew ran Claude’s waypoints by means of a simulation they use day-after-day to verify the accuracy of instructions despatched to the rover. Ultimately, NASA says it solely needed to make “minor adjustments” to Claude’s route, with one tweak coming because of the actual fact the crew had entry to ground-level photographs Claude hadn’t seen in its planning course of.
“The engineers estimate that utilizing Claude on this approach will lower the route-planning time in half, and make the journeys extra constant,” NASA mentioned. “Much less time spent doing tedious handbook planning — and fewer time spent coaching — permits the rover’s operators to slot in much more drives, acquire much more scientific knowledge, and do much more evaluation. It means, briefly, that we’ll be taught far more about Mars.”
Whereas the productiveness features supplied by AI are often overstated, within the case of NASA, any device that might enable its scientists to be extra environment friendly is certain to be welcome. Over the summer season, the company lost about 4,000 employees – accounting for about 20 % of its workforce – resulting from Trump administration cuts. Going into 2026, the president had proposed gutting the company’s science funds by nearly half earlier than Congress finally rejected that plan in early January. Nonetheless, even with its funding preserved slightly below 2025 ranges, the company has a troublesome street forward. It is being requested to return to the Moon with less than half the workforce it had throughout the peak of the Apollo program.
For Anthropic, in the meantime, it is a main feat. It’s possible you’ll recall final spring Claude couldn’t even beat Pokémon Red. In lower than a 12 months, the corporate’s fashions have gone from struggling to navigate a easy 8-bit Recreation Boy sport to efficiently plotting a course for a rover on a distant planet. NASA is worked up about the potential for future collaborations, saying “autonomous AI methods may assist probes discover ever extra distant components of the photo voltaic system.”